Top 5 Security issues with cookies
Computer cookies, for the most part, are beneficial to your online experience. They help websites provide personalized experiences for each user—which is incredible, considering the number of online users. But like anything online, hackers, cybercriminals and bad actors have discovered ways to utilize cookies to take advantage of people.
Before diving into the specific security issues with cookies, it’s important to understand the different types.
Computer cookies can be broken down into three categories:
Session cookies
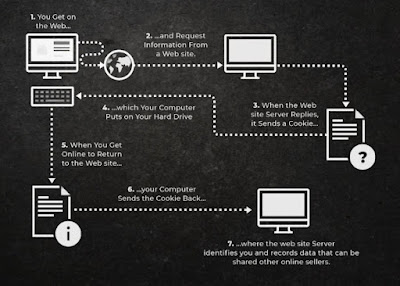
What are cookies ?
Cookies are the text files with small pieces of data like username and password that are used to identify your computer as you use a computer network.
Types of cookies:
1. Session of cookies :
If you visit website requiring a password, session cookies are what allows you to hop from page to page without needing to log in every time.
2. Persistent Cookies :
Persistent cookies are used to update your perferences when you visit a website. They're used to analyze a user's browsing habits.
3. Flash Cookies :
Similar to persistent cookies, except they're stored as abode flash files instead of text files, these contains the same data and work just like other cookies.
Five security issues with cookies -
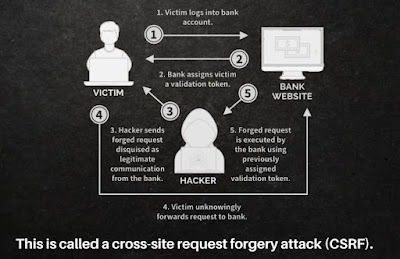
1. Cross-site request forgery attack (CSRF)
It is an attack that forces authenticated users to submit a request to a web application against which they are currently authenticated.
CSRF attacks exploits the trust web application has in an authenticated user.
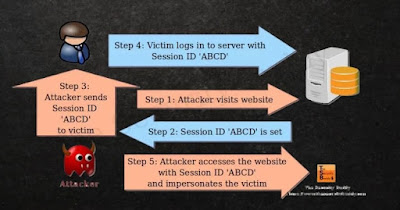
Session Fixation
If a website allows session IDs in the query parameters, an attacker can include a specific session ID in the URL.
If they send that URL to a user and the user logs info the website using their legitimate credentials, the attacker can then take over that session and gain access to the user's account.
Cross-Site scripting (XSS)
The attacker writes malicious code and post it to a trusted website. When the user visits the website, their browser is loads the content.
It executes all the scripts and grants access to any session tokens, cookies, or other sensitive information including login details.
Cookies Tossing Attack
Attackers create a fake subdomains cookies for a website and send it to a user. When the user visits that website.
It'll pull the attackers fake cookies, then attackers will be able to take over the session and gain access to the user's account.
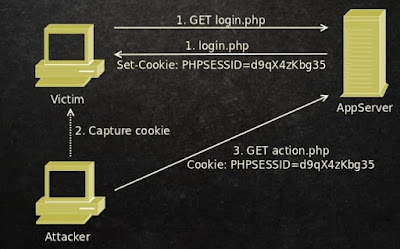
Cookies Capturing
If a cookie is being used for authentication purposes should always be sent via secure SSL/TLS channels.
If a website allows for cookies to be sent using cleartext, an attacker could potentially eavesdrop on network traffic to capture the unsecured cookie.
Conclusion
Cookies have made a significant contribution to making the web stateful, but they also add to the attack surface.
They can be used by hackers to gain control of privileged functionalities perform SQL injections, session hijacking, and account takeover.